Many people turn to medication to reduce swelling and pain. Yet, there are also ways of fighting inflammation at the root cause. Here you will learn how to reduce chronic inflammation naturally. One of the best ways to do this is to start with your diet.
If you’ve suffered from arthritis, irritable bowel syndrome, eczema, hay fever, or chronic pain you know how harmful inflammation can be. Inflammation causes your body's soft tissues to swell up with blood and water. This swelling can be very painful. Furthermore, it may do further damage to your body, causing even more inflammation.
Acute Inflammation vs Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation that happens once in response to a threat and then goes away is called acute inflammation. Inflammation that doesn't go away on time is considered chronic. There are some key differences between the two.
Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation is reacting to a one-off threat, which the body gets rid of quickly. Acute inflammation lasts no longer than a few days.
Acute inflammation calls in a wide variety of specialized cells, some lighter ones, some heavy-hitters, and wipes out the attack. Acute inflammation has three potential results. It can resolve the condition, and everything goes back to normal except for maybe a bit of scar tissue. It can kill all infected and damaged tissue, but also the infection, resulting in an abscess. The abscess may collect pus and become secondarily infected, but if treated well it may heal over. Or, finally, acute inflammation can keep on going and turn into chronic inflammation.
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation almost always sets in after acute inflammation has failed to resolve the problem. The results of chronic inflammation are always harmful. It will destroy tissue, resulting in an abscess or ulcer which will not heal, because the new, healthy cells keep getting attacked.
Chronic inflammation lasts anywhere from months, to life and can be because:
- The threat is too strong for the immune system to defeat, due to a virus that has taken full control of the body.
- There are many dangerous foreign bodies that can't be got rid of.
- The immune system is making a mistake and attacking normal or healthy cells (known as an auto-immune condition).
Chronic inflammation will also cause fibrosis and necrosis. It can kill healthy tissue until it begins to scar and rot inside the body, slowly stopping your organs from functioning.
Chronic Inflammation Increases Health Risks
Why You Should Be Aware of Chronic Inflammation
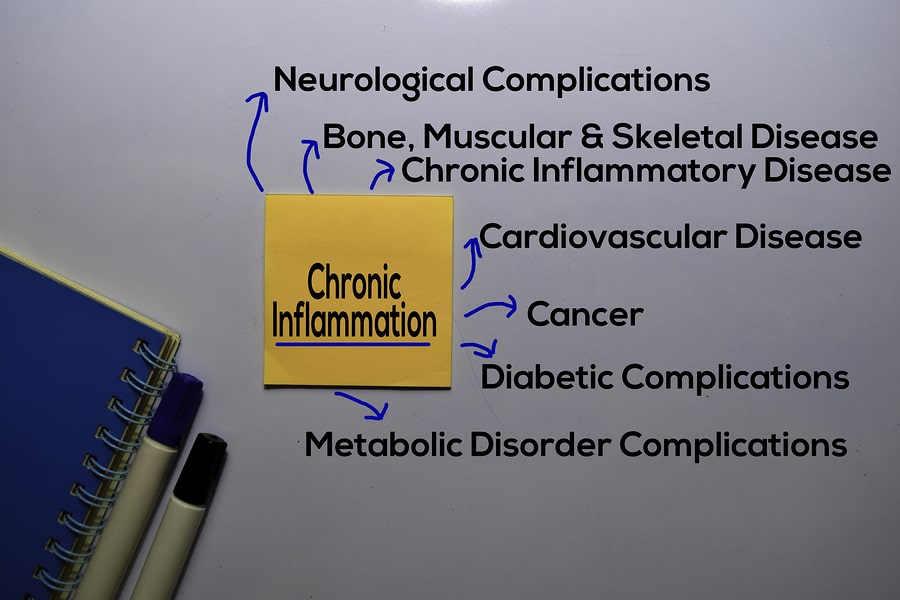
As we have seen above, chronic inflammation directly causes many conditions. But it also increases your risk of others and makes some ailments worse when you already have them.
Fibrosis
Chronic inflammation causes fibrosis. Fibrosis is where connective tissue starts growing excessively and invades other tissues in your body. Normally this is a healthy mechanism, like scarring after an injury. But when inflammation causes scarring and tears in the tissue, it can stop your organs and muscles from working properly.
Cancer
Chronic inflammation increases your risk of cancer by promoting rapid cell proliferation. When your cells are inflamed and multiply quickly, there is a greater chance of a mutated cell being formed. And when your immune system is taxed, this mutated cell may be allowed to multiply out of control, resulting in cancer.
Heart Disease
Chronic inflammation increases your risk of heart disease. Swelling hardens your blood vessels and pumps up your heart, increasing blood pressure and limiting your ability to increase your heart rate. The two together put you at risk of a heart attack, even if you are slim and otherwise healthy!
Diabetes
Chronic inflammation increases your risk of diabetes. Inflammation affects your body's insulin production, resulting in hypersensitivity or insensitivity to glucose, raised blood sugar, and a high predisposition to diabetes.
Alzheimer's
Chronic inflammation increases your risk of Alzheimer's. High blood pressure, a weak immune system, and a predisposition to diabetes put you at risk for dementia. Inflammation around the brain increases the risk of plaques forming in the brain, which is a key cause of Alzheimer's.
Obesity
Chronic inflammation makes obesity worse. When you are obese, every bit of movement you can get improves your health. So naturally, when your organs are taxed, your joints are sore, your blood pressure is up and you're storing water weight, you will suffer the effects of obesity even more. This can create a cycle of ill health, as obesity also causes inflammation. (How to Lose Weight With Ayurveda)
Insomnia
Chronic inflammation makes insomnia worse. If you suffer from insomnia, inflammation will make you sleep poorly. People who sleep well at night have less inflammation than people who have difficulty sleeping. Poor sleep is not just a sign of ill health but causes other complications.
Osteoporosis
Chronic inflammation makes osteoporosis worse. It won't give you osteoporosis, but too much swelling stops your body from repairing bones properly, resulting in less robust bones. If your bones are brittle from osteoporosis already, then inflammation may make them even more likely to break.
Chronic Inflammation and Ayurveda

Ayurveda is one of the oldest healing systems developed in India more than 5000 years ago. The healing science classifies inflammation as an imbalance of the Pitta dosha (the principle of fire). With simple adjustments to your diet, daily routine and herbs you can cool and cure chronic inflammation.
Fire governs all transformation in the body and is responsible for appetite, digestion, hormones, brilliance, and luminosity. As you can see the principle of fire is a necessary ingredient to good health. But when your fire burns too hot or flares up in the wrong places , the result in chronic inflammation.
Here are the diet lifestyle tips to balance your metabolic fire: Pitta Reducing Diet and Lifestyle
Foods That Cause Inflammation

Even if you have no food allergies at all, some foods cause and prevent inflammation in us all. If you want to stay as healthy as possible and keep inflammation down, consider eliminating or significantly reducing these foods from your daily diet:
Sugar
If we eat too many foods containing simple sugars like glucose, sucrose, or even fruit sugars like fructose, our body suffers inflammation. Here's what happens when you quit eating sugar.
Most of this inflammation is internal, so you won't notice any swelling on the outside unless you were already suffering from external inflammation!
But your blood will show inflammation markers, and if you have arthritis, eczema, or any other superficial inflammation, you will notice it get worse the more simple sugars you eat.
What's more, simple sugars also harm our white blood cells, so not only are we suffering inflammation, but our healthy inflammation is less able to fight threats! This is in part why diabetics in a state of hyperglycemia are at risk of losing body parts when they get a sore or an injury.
Refined Carbohydrates
Yep, and for the same reason as sugars. Refined flour, oats, or mashed potatoes, for example, are all very simple carbohydrates.
They might be a starch on your plate, but in your mouth and stomach they quickly become simple sugars again, so you may as well be eating candy. For this reason, many researchers have suggested not just eliminating sugar from our diets, but monitoring the Glycemic Index or Glycemic Load of our foods if we want to control how much sugar we're getting.
The Glycemic Index tells you how long it takes for the sugars in a food to reach your bloodstream. Whereas the Glycemic Load assesses how much sugar is in your blood based on the Glycemic Index of the food multiplied by the grams of carbohydrate it has.
Both are good ways of avoiding inflammation. Checking the Glycemic Index will tell you which foods are dangerously sugary, and checking the Glycemic Load will tell you whether you have eaten too many carbohydrates, even if they are low on the Glycemic Index.
Artificial Sweeteners
Sorry, but we're having to take this one away too!
A study has found that giving humans artificial sweeteners can cause glucose intolerance and promote type 2 diabetes. This reaction is also responsible for the production of cytokines, which cause heavy inflammation all through our bodies.
Not only that, but they attack our good gut bacteria, causing inflammation and pain through our lower digestive tract. Here's more on the harmful effects of artificial sweeteners. If it's any comfort, combining honey with fatty food to produce a low-GI meal can make a wonderful anti-inflammatory pudding.
Salt
Salt affects inflammation in two ways. Firstly, it promotes high blood pressure, which can cause or worsen inflammation. And secondly, the fluid retention it causes worsens inflammation you already have.
Although a small amount of salt for a healthy person is no problem at all, and salt can be bad news for someone who already suffers from inflammation. Too much salt can cause inflammation in even the healthiest of people. And some salts, like nitrates, can cause inflammation all on their own.
Refined Oils
Plant oils aren't necessarily bad for you. In fact, many minimally processed oils from seeds (like sunflowers), nuts (like walnuts), and fatty fruit (like olives) are actually good for you. They provide a healthy dose of essential fatty acids (EFAs).
Researchers have found that processed oils, like vegetable oils, or corn oil, and many other seed oils, are rich in omega 6 EFAs. Normally this is fine, but if you have too much omega 6 and too little omega 3 and omega 9 you can suffer inflammation.
This isn't anything to do with the EFA, but with the ratio! You should ideally eat a 1:1:1 ratio of omegas 3, 6, and 9. That means that for every gram you have of one, you should have a gram of the other two. Any imbalance causes inflammation.
So, don't chug omega 3 and cut out your plant fats entirely. Studies have recently shown that people who have many omega 3 supplements and avoid omega 6 also end up with inflammation!
Grain-fed Animal Fats
Although saturated fat has recently been found to not cause heart disease in healthy people, that doesn't mean you should be eating all the fat off your ham and frying everything in butter.
You need to know where these animal fats have come from. Grain-fed animals produce saturated fat that has been proven to cause as much inflammation as vegetable oils. If you want to be healthy, stick to the natural stuff.
Well-cooked Meats
BBQ meats and processed red meats, are chock full of advanced glycation end products, an inflammatory compound that happens when you cook protein too long and too hot.
Grains
Many more people than we previously thought are turning out to have an intolerance to gluten. Although gluten sensitivity is a myth, gluten allergies are very real and cause severe and painful inflammation and bleeding in sufferers.
But what if you feel unwell after eating bread, but aren't allergic to gluten?
Until very recently we used to make bread with complex yeasts almost always. These yeasts would pre-digest our grains, breaking down the gluten and other complex, gut-irritating proteins. Even if you are gluten-tolerant or eating a gluten-free grain like corn, you may find your body has an inflammation reaction to the unprocessed proteins in the loaf! If you're gluten-tolerant, strive to eat yeast-risen bread and sourdoughs.
Dairy
Approximately one in four adults have difficulty digesting any sort of milk, either lactose, casein, or whey. It is also considered possible that half the human population or more has difficulty digesting cow's milk. If you have trouble with dairy, check out this Ultimate Guide to Going Dairy Free.
These irritants cause inflammatory reactions akin to an allergy. There is typically swelling in the intestine, so if you bloat after eating dairy, you may have difficulty digesting it. It's thought that most people who have trouble with cow's dairy can digest goat's dairy products just fine though. Which is good news because the probiotic anti-inflammatory benefits of fermented dairy are actually many.
Nightshades
Nightshades describe all plants from the same family as the deadly nightshade. And it may surprise you, but we eat a lot of them! Potatoes, tomatoes, peppers of all varieties, zucchini, eggplants… a whole array of foods belong to the nightshade family. And, annoyingly, they do still contain some of the same toxins!
That's why potato greens, for example, are poisonous. The amount in the parts we eat is a very low dose, which is good news. It's like the fact that there is cyanide in apple seeds, but we don't worry about swallowing one because we'd need to eat a plateful to feel any effect.
But the bad news is that some of us are more sensitive to nightshade toxins than others. Many of us can chow down on tomatoes as much as we like, some of us may have a minor allergic reaction to all nightshades, resulting in inflammation.
Alcohol
Although like with all fermented foods a little bit of alcohol a couple of times a week keeps our gut bacteria healthy and strong, drinking daily has the opposite effect.
As we turn alcohol into sugars, our pancreas produces enzymes to digest the alcohol, our liver filters out toxic byproducts and passes them on to the kidneys to excrete. If you have too much alcohol, one of these organs is eventually going to have too much work on its hands, resulting in a buildup of toxins that will cause inflammation.
Plastic-sealed Foods
You know how nobody wants plastic Tupperware, cutlery, or plates unless they're certified BPA-free? Do you remember why that was?
BPA is a phthalate-type compound that breaks down when heated and leaves toxic particles in your food. Well there are loads of different phthalates used in the packaging of plastic-sealed foods, and they're dangerous. And how do they get the plastic on? With heat, of course! Meaning that even if it's all removed before the food is cooked, it's too late: the phthalates are already in your food.
Fast food restaurants typically transport their pre-prepared ingredients in these plastics. Many of your favorite store-bought processed foods come in them, from microwave meals to pates. Ouch.
Artificial Additives
In this case, when we say “artificial” we mean something that would not be found, in that state, in nature.
In much the same way steel might occur naturally. But when we make stainless steel ourselves, these additives may resemble natural things but are heavily altered. Many artificial colors and flavors disrupt our natural hormones and trigger histamine release. As our bodies don't recognize these products, we start the inflammation response to try and get rid of these strange invaders as soon as possible. Furthermore, many emulsifiers inhibit our natural digestion of fats, upsetting our gut balance and causing inflammation.
So those are the foods you absolutely, positively want to avoid if you don't want to suffer inflammation. So, the question is: what can we eat when we're prone to chronic inflammation?
How to Reduce Chronic Inflammation Naturally
Eat These Abundantly

Beets
The humble beet is an amazing source of phytochemicals, which give it its bold, stain-prone color. Betaine, one of the most powerful, is very anti-inflammatory. It improves metabolism, reduces the impact of glucose excesses in the blood, elevates your mood, and encourages fat burning.
Eating beets regularly is great for you. For best effects, eat a combination of raw and cooked beets, each one once a week. Some elements of them are healthier raw, and others when cooked, so mixing and matching is perfect. For your cooked beets, try some hearty beetroot soup, Eastern European style, as borscht. And for your raw ones, grate or chop finely into a salad.
Dark Chocolate
Cocoa is loaded with antioxidants that prevent weight gain, water retention, and inflammation. Bacteria in our guts ferment chocolate's fats into amazing compounds that reduce insulin resistance and cut down on inflammation. But reach for dark chocolate with a cocoa content of 75% or above, as both milk and sugar are inflammatory. For best effects, have pure cocoa powder in a drink like coffee, or have 99% cocoa chocolate with some fibrous fruits, to promote healthy fermentation.
Chia Seeds
Almost all seeds are amazing for you, so don't take this entry to mean that you need to stop eating sunflower, pumpkin, or flax seeds. But if you aren't already eating them, chia seeds are a great addition to your diet. They stabilize blood sugar, help you lose weight, balance blood pressure, and reduce salt absorption, making sure that your inflammation stays within healthy boundaries.
For best effects, eat them whole and raw on top of cereal, crush into butter for your bread, or soak them and blend them into a smoothie.
Apples
Probiotic foods are essential to gut health, but less known are prebiotics. Where probiotic food adds healthy bacteria to your gut, a prebiotic feed these bacteria. Apples are naturally rich in starches and fiber, making them a great prebiotic. But they are also full of pectin and antioxidants, mostly contained in their skins, which directly attack inflammation. But be careful, as apples can be very high in sugar, and not all varieties have as much antioxidant content as others.
For best effects, choose slightly bitter apples, like granny smiths or russets. If you can stomach them, Crabapples and Braeburns are the very best!
Berries
Berries are nature's very own anti-aging medicine. They're chock full of anthocyanins and flavonoids that assist in digestion and reverse the process of inflammation.
They have actually been shown to turn off the genes responsible for inflammation and auto-immune reactions, making them great for people with common allergies and auto-immune conditions! And their high content of vitamin C and resveratrol helps remove free radicals, which also reduces inflammation.
For best effects, choose berries with dusty-looking skins and eat a cup of them fresh every day.
Tuna
White tuna, or skipjack tuna, is very high in omega 3. If you're on a budget and can digest fish, this may be the best and healthiest way of increasing your omega-3 intake. And as it has a natural omega oils balance it's perfect for supplementing. To get the most benefits, choose fresh tuna and have it lightly cooked, or raw if you can source sushi-grade tuna. But if your budget doesn't stretch that far, simple tuna in olive oil is a perfect oil supplement.
Nuts
Nuts are a great source of all omegas and contain them in a very healthy balance. They're also your best plant-based source of omega 3. Not only that, but they're rich in Vitamin E and oleic acid, which both reduce inflammation. The best ones are walnuts, hazelnuts, and brazil nuts. Make sure to eat raw, unsalted nuts for the highest benefits, and don't fall for peanuts: they're actually a legume and are actually mildly inflammatory.
Spinach
Unfortunately, spinach's fame as an iron-rich superfood is a myth caused by a printing error. But the good news is that it is absolutely loaded with all sorts of other micronutrients which help in decreasing harmful inflammation. Carotenoids and Vitamin C, Vitamin E, as well as Vitamin K are abundant in spinach and help fight inflammation, especially in your internal organs.
For a healthier, less inflamed heart, liver, and kidneys, eat ten cups of raw or lightly steamed spinach a week. But if you want to eat more, feel free to eat as much as you like.
If you have concerns about oxalates or have a history of kidney stones known to complicate eating oxalate-rich foods, talk to your health care practitioner for advice.
Green tea
Green tea has been a popular drink for older people and ill people across the East for millennia. And for good reason! It is chock full of micronutrients that reduce the effects of aging and fight inflammation by strengthening your immune system.
For best results, steep green tea in water just below boiling temperature (if you can hold your hand over it, but not put it in, it's perfect), and drink three mugs a day, before meals if possible.
Broccoli
Pretty much all the brassicas are full of glucosinolate. Not only is broccoli rich in this inflammation-fighting compound, but it is accessible and mild-tasting compared to its brothers: kale and Brussel sprouts. It's also rich in vitamin K, which regulates how much inflammation you suffer, ensuring your inflammation levels are healthy. But beware: as it's a flower it could trigger a pollen allergy. Cook this vegetable well before serving.
Wild Salmon
Wild salmon is amazing food, simply because of its rich omega 3 content. As we've mentioned, chowing down on omega 3 supplements could have the opposite of the desired effect when we're trying to have a healthy balance of omegas 3, 6, and 9, skewing the ratio the other way and promoting inflammation.
By eating our omega oils in foods, as opposed to in pure oil form, we make sure we have a healthy balance. For best results, eat your salmon lightly steamed, or buy sushi-grade salmon and eat it raw, preserving all the oils in the fish.
Pineapple
This tropical fruit is an amazing source of bromelain. Bromelain is actually the reason pineapple and meat pair so well, as this enzyme helps to pre-digest meat for you. But it's also a powerful anti-inflammatory agent! It doesn't act on inflammation itself, meaning it is safe for people whose inflammation is benefiting them.
Instead, it fights pro-inflammatory metabolites and helps to clear salt-based water retention. This takes the edge off unhealthy chronic inflammation and speeds up recovery if you've had a hard day at the gym, but doesn't stop our natural, healing inflammation. For best results, have thinly sliced raw pineapple with pork, or some chunks in a salad. But don't eat too much if your diet is rich in other sugar sources!
Olive Oil
Another great source of omega oils, as well as oleic acid. Extra virgin olive oil has countless individual properties as well, such as containing oleocanthal, which enhances its immune-system strengthening abilities. It prevents the production of inflammatory enzymes, regulates our immune system, and, just as importantly, stops us from using inflammation-causing oils and fats like vegetable oil or common lard. However, beware: it has a very low smoke point, so for best results, you need to use this oil for low-temperature cooking, as an addition to soups, and cold on salads and bread.
Coconut Oil
So, what happens if you want to fry something properly? Fear not, you don't need to turn to inflammation-promoting oils. Coconut oil is full of anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce the inflammation associated with injuries and infections but doesn't target chronic inflammation. But reducing acute inflammation helps prevent developing chronic inflammation, which is definitely a plus. And coconut oil has a very high smoke point, meaning you can fry things in it at a very high temperature without creating dangerous trans fats.
Bones
It may seem like a hipster foodie fad, but bone broth is really great for your immune system. The cooking process extracts collagen and glucosamine, which help in recovery and boost your immune system, reducing the need for natural inflammation by healing damage quickly. It also contains some advanced glycation end products, though, from the extended cooking. However, research seems to show that the benefits outweigh the problems. For the greatest benefits, have a cup of bone broth with herbs in it every day.
More here on how to change your diet to relieve chronic pain.
The Complete Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Beginners: A No-Stress Meal Plan with Easy Recipes to Heal the Immune System
Treat These as Complementary Medicine
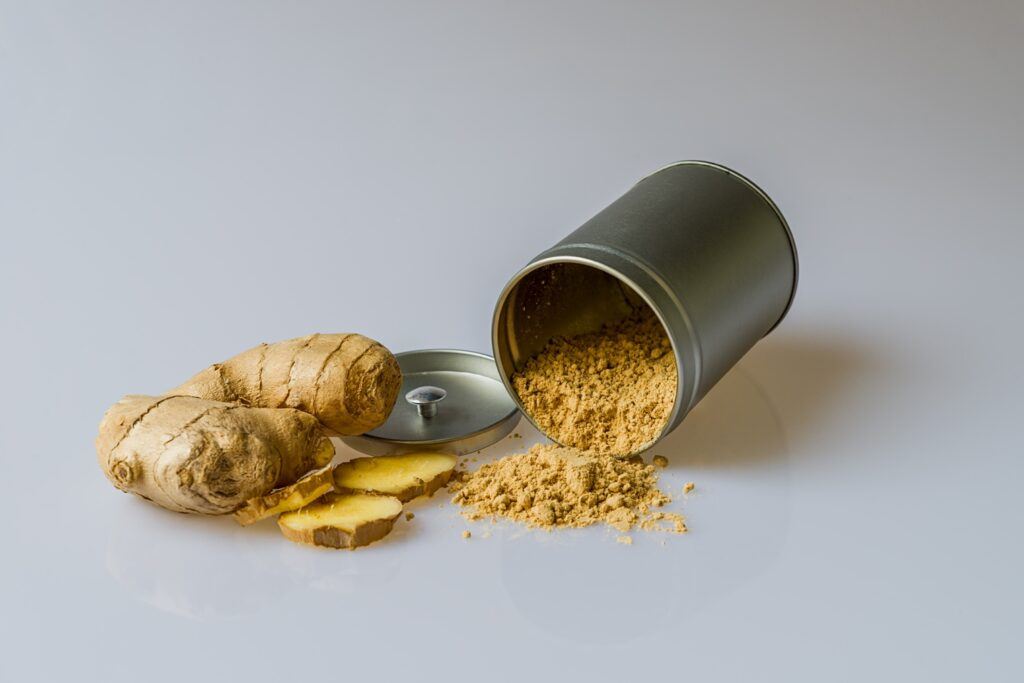
Raw Ginger
Research has found that raw ginger has many compounds called gingerols which are simply amazing. They're antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and help fight disease. They block many genes and enzymes that are causes of inflammation. A small dose is wonderful for people with swelling in their joints and muscles.
But you can't just chow down on raw ginger daily. Their effect is so powerful that a heavy dose will reduce healthy inflammation as well, making illness last longer and leaving weak joints unprotected.
For best effects, have 10ml of extracted ginger juices, or 20g of grated fresh ginger in a smoothie or salad dressing. But if you're a true ginger lover, feel free to indulge in as much cooked ginger as you like: the cooking process breaks down the antioxidants and enzymes, making it ineffective, but also harmless.
Garlic
Do you know how garlic makes colds and flu feel so much easier? That's because they are a powerful anti-inflammatory food. They are loaded with allicin, a common compound in all alliums (onions, garlic, spring onion, leeks…) but especially abundant in garlic.
Aged garlic provides the best effects, but the next best thing is raw garlic. For best effects, mix raw minced garlic with a little olive oil and vinegar and use it to dress a salad or season cooked chilled meats and starches. A chicken salad with a raw garlic dressing could do you wonders.
But don't make this an everyday thing, especially if you already take anti-inflammatory medicines, as the compound effect might be too powerful and reduce healthy inflammation. And beware garlic if you are over fifty as if you are one of many people who develop a sensitivity to alliums as you age. It can disrupt your gut balance, provoking inflammation and undoing all your hard work.
Coffee
Coffee, unsurprisingly, boosts your metabolism. Actually surprisingly, it's full of antioxidants that reduce inflammation and promote a healthy immune system. But it is a very strong anti-inflammatory food too, and also a strong stimulant. This means that it can increase blood flow, attack healthy inflammation, and raise your blood pressure. So, talk to your doctor before using coffee as a supplement. One cup of strong coffee a day is more than most people need to feel the benefits.
Rosemary
This traditional cooking herb has a very high concentration of anti-inflammatory antioxidants. It also contains carnosic acid and other compounds which inhibit the production of cytokines. This herb is great cooked or raw and will help keep your heart, liver, and kidneys healthy. But be careful with it. It's highly effective, so much so that rosemary extract can act as a preservative! So, consult with your doctor, and only use it sparingly for a bit of anti-inflammatory help.
Turmeric
Turmeric directly inhibits inflammation pathways from operating by attacking the enzymes that drive them. It contains curcumin, a compound with strong anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation and pain in the body. However, curcumin on its own is poorly absorbed into the bloodstream.
Adding black pepper, which contains piperine, significantly enhances curcumin's absorption by up to 2,000%. Piperine achieves this by inhibiting certain intestinal enzymes, thus increasing curcumin's bioavailability and, consequently, its effectiveness in reducing inflammation. This is the formulation I swear by because it works!
Honey
Although it is also a sugar, honey has many anti-inflammatory properties as well. This is because it contains proteolytic enzymes. These enzymes control your body's natural anti-inflammatory responses, activating them and shutting down unnecessary inflammation. It relieves problems such as IBS, and the symptoms of food intolerance pains. It is also, unlike other sugars, full of antioxidants, carotenoids, polyphenols, and vitamins. But it is still a rich source of sugar, so limit your consumption to a teaspoon or two a day.
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is famous for its anti-inflammatory factors. Its active compound is amazing for heart health and holds the key to anti-inflammation naturally. Something about cinnamon also has been linked to making red blood cells a little less “sticky,” and platelets are less likely to form clots.
Brahmi
Brahmi or Bacopa monera is an ancient Ayurvedic herb and one of the best herbs for balancing and rejuvenating Pitta dosha.
Boswellia
Boswellia or Indian Frankincense is a resin from the Boswellia tree. It has anti-inflammatory properties that can help with inflammation.
How To Reduce Chronic Inflammation Naturally Conclusion
Since chronic inflammation is a major cause of most illnesses, it is imperative that you reduce foods that have an inflammatory effect and increase those that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
By following these general guidelines on how to reduce chronic inflammation naturally you will be able to reduce inflammation in your body. Combined with other healthy lifestyle factors you can reduce your risk of weight gain, premature aging, and chronic disease.
Best dietary advice in 7 words: “Eat food. Not too much. Mostly plants.” Michael Pollan
Don't forget to like us on Pinterest. Thank you for your time and reading.
The information presented here is in no way meant to serve as medical advice. If you are experiencing symptoms of any kind, please consult with your physician.