There are claims you can boost your immunity by eating particular foods. But do they stack up?
A healthy, balanced diet is important for supporting your immune system. You need sufficient energy and nutrients for the immune system to function properly, and poor nutrition can compromise it.
But there is “no individual nutrient, food or supplement that will boost immunity, or stop us getting highly infectious viruses like Covid-19,” says Sarah Stanner, Science Director at the British Nutrition Foundation.
So do you need to make changes to your diet for the sake of your immune health?
The importance of five a day

Aim to eat a wide range of fruit and veg to ensure you get all the nutrients your immune system needs. “Each micronutrient plays a different role in the immune system – don’t make a hero of just one,” says Stanner.
Fruit and veg are packed with vitamins, minerals and chemical compounds known as phytochemicals. These can be converted by your gut microbes into beneficial metabolites that fight inflammation in the body.
The colour of a plant is determined by the phytochemicals it contains, and some of these are associated with positive benefits for the immune system. The wider the variety of different coloured plants you eat, the more types of phytochemicals you’ll consume.
Red, orange, yellow and green plants contain carotenoids, which have been associated with boosting immunity. Evidence for the benefits of phytochemicals to immunity is not conclusive, but there is no health downside to eating five a day.
If buying fresh ingredients is tricky because you’re shopping less frequently than before the crisis, put some frozen or tinned fruit and veg into your trolley – frozen can be more nutritious than fresh because it’s frozen so soon after picking.
Tinned fruit and veg, including beans and lentils, count towards your five a day, but be careful to choose tinned fruit with no added sugar.
Support your gut with different plant fiber
Research suggests a connection between the bacteria in your gut and the functioning of your immune system. The wider the variety of plant fiber you eat, the healthier and “more diverse” the bacteria in your gut will be.

The optimum level of variety is eating 30 different types of fruit and vegetables per week, including nuts, seeds and herbs. But there are additional ways to support your gut bacteria via diet.
Vegetables are a type of prebiotic, a group of fibre-containing foods that ‘fertilise’ existing bacteria and encourage microbe development. Other prebiotics include wholegrain foods, such as brown bread, rice and pasta, beans and pulses.
Eating probiotics, such as live yoghurt, quality cheese (not the ultra-processed stuff) and fermented foods, encourage more microbes to grow. But it hasn’t been proven that they reach the gut.
But do limit ultra-processed foods, sugars, sweeteners and preservatives, as they have be found to reduce the diversity of bacteria in your gut.
Food vs food supplements
Supplement sales received a massive boost during the pandemic. But you can absorb more nutrients through whole foods than through supplements, and phytochemicals cannot be replicated by supplements.
However, a multivitamin can be helpful if you are not getting all your nutrients from your diet or are unwell. Vitamin C supplements are popular, and this vitamin is very important for the immune system, but in reality few people are deficient in it.
What are nutrients for immunity?
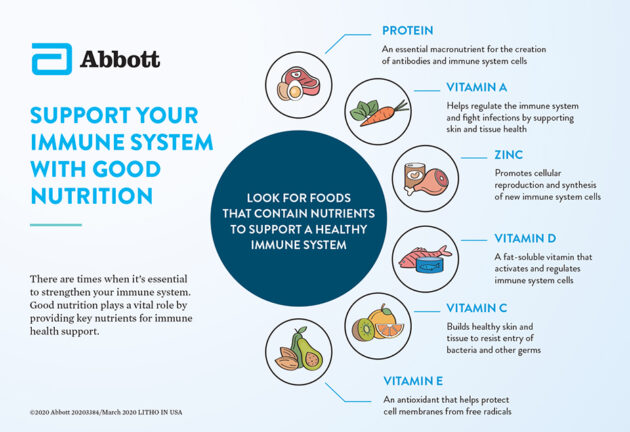
The following nutrients are important for normal immune function:
- Vitamin A supports T Cells (a type of white blood cells). Your body converts beta carotenes from foods such as yellow, red and green (leafy) veg, carrots, sweet potatoes, red peppers and yellow fruits, into vitamin A. Liver, whole milk and cheese contains retinol, a preformed version of vitamin A.
- Vitamin B6, B12, folate, selenium and zinc help produce immune cells. B6 is found in poultry, fish, egg and bananas. B12 is found in meat, salmon, cod, milk, cheese, eggs and fortified foods contain. Folate is found in green vegetables, pulses, nuts and seeds. Selenium is abundant in Brazil nuts, fish, meat and eggs contain selenium. Zinc is found in meat, shellfish, dairy, bread and cereal products such as wheatgerm.
- Copper helps protect and fuel immune cells. Nuts, shellfish and offal are good sources.
- Iron helps immune cells stay healthy. Research shows females aged 11-49 are the most likely group to consume below the recommended amount of iron. Iron can be found in red meat and fish. Plant-based sources of iron (called non-heme iron), including wholegrains, nuts, beans and dried fruits, but aren’t as easily absorbed.
- Low levels of vitamin D are associated with reduced immune response. Our skin makes vitamin D from the sun, which is why taking a supplement is advised through autumn and winter.
- Here are 25 additional ways to Boost Immunity
So now you know everything you need to enhance your immunity with a healthy diet. Thank you and Happy New Year!



