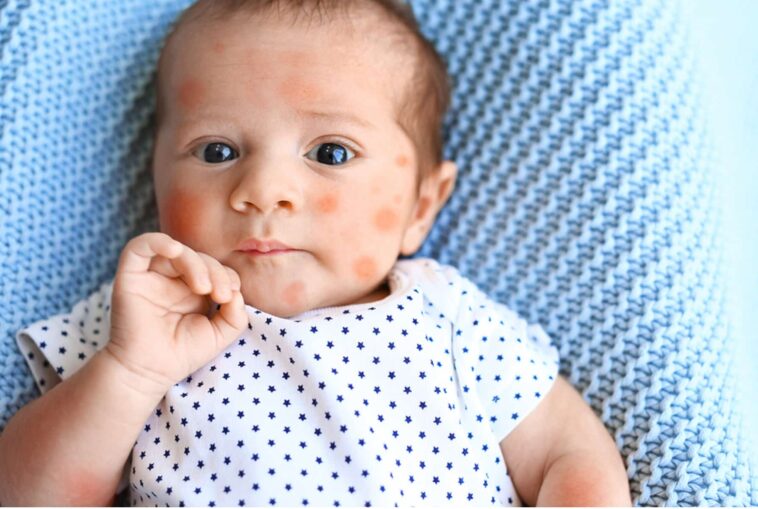
Warning: This is not your average advice on what is baby eczema and how to cure it. You will not find the generic (and nearly useless) information that you typically find on pediatric and medical websites. Although those websites help you diagnose your baby, it rarely gives you any substantial remedies that get to the root of the issue.
I will not be prescribing any medication or topical creams to soothe the painful rashes that your baby is currently suffering. I will equip you, as the parent and caretaker, with real-life practical and healing knowledge. This is not surface-level information. This goes deep. If you are ready to continue, read on.
What Is Baby Eczema Exactly?
Eczema (EK-zeh-ma) is a non-contagious condition that tends to come and go where the skin gets irritated, red, dry, bumpy, and itchy.
There are several types of eczema, but the most common is atopic dermatitis. The skin can leak fluid and then crust over especially when scratched due to the high itchiness of this condition.
It’s often found on infants' cheeks, forehead, or scalp. It may spread to the knees, elbows, and trunk (but not usually the diaper area).
Older kids and teens usually get the rash in the bends of the elbows, behind the knees, on the neck, or on the inner wrists and ankles.
What Causes Baby Eczema?
Doctors don't know exactly what causes eczema. They don't know what is baby eczema. And they say there is no cure, only treatments that help with symptoms.
Thank goodness we can go beyond the answer medical doctors give us because when our baby is hurting that answer is unacceptable.
Before we continue with how to cure eczema at home, we need to understand how our skin is created and from where it is controlled in the brain.
Then we will look into German New Medicine via biological conflict experienced in people living with eczema. We will then close with the healing phases necessary to cure eczema.
Let’s dive in!
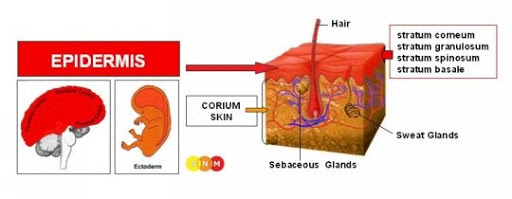
Development and Function of the Epidermis
The epidermis is your outer skin and it is composed of 4 layers.
- stratum basale
- stratum spinosum
- stratum granulosum
- stratum corneum
The epidermis is predominantly responsible for sensory perception such as temperature, pressure, and touch. Most cells in the epidermis are keratinocytes (keratin-producing cells) that originate in the deepest layer of the epidermis.
From there, keratinocytes migrate through each layer of the epidermis until it reaches the surface layer. Then, they are gradually shed and replaced by newer cells pushed up from below.
The epidermis consists of keratinized squamous epithelium, originates from the ectoderm, and is therefore controlled from the cerebral cortex.
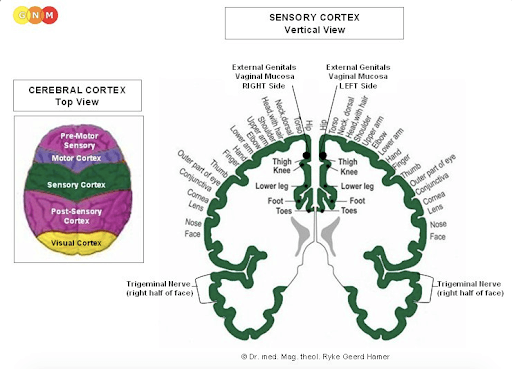
How the Skin is Controlled at the Brain Level
The epidermis is controlled by the sensory cortex, which is a section of the cerebral cortex. The skin of the right side of the body is controlled from the left side of the sensory cortex; the skin of the left side of the body is controlled from the right cortical hemisphere.
What is a Biological Conflict and Which One Does My Baby Have?
To understand what is baby eczema, you must understand what is a biological conflict.
A biological conflict is an unexpected, highly acute, and isolating conflict shock that occurs simultaneously in the psyche, the brain, and on the corresponding organ. The biological conflict linked to the epidermis is a separation conflict experienced as a loss of physical contact.
Newborns suffer the conflict when they are separated from the mother at birth, for example when they are put in an incubator or given up for adoption.
A separation conflict can already occur intrauterine because of ultrasound procedures. The ultrasound noise drowns out the heartbeat of the mother, which can be highly traumatic for the fetus; each ultrasound test triggers a conflict that relapses for the unborn.
For an infant, the mother is the most important attachment figure; the mother protects her child and can prevent conflicts from happening. Hence, when a small child has a separation conflict, the mother was usually absent when the biological conflict occurred.
Separation Conflict Triggers

Children also experience separation conflicts when:
- they are scolded, punished, or abused
- a new sibling is born who gets more attention
- the parents split up
- they are not allowed to see their friends
- they have to separate from a favorite doll, teddy bear, stuffed animal, or pet they like to cuddle
- the mother goes back to work
- they are put into daycare, kindergarten, or to relatives or when they are left with a sitter or nanny.
By the same token, the separation conflict refers to wanting to separate from a person in the sense of wanting but not being able to push someone away (literally or figuratively).
For example, a terrorizing family member or teacher, an annoying schoolmate, or an abusive parent.
A separation conflict also pertains to wanting to separate from something close to the skin (face mask, oxygen mask, a helmet, hat, clothing, shoes, tight stockings, wet linen, wet diapers).
The Outer Skin Sensitivity Pattern
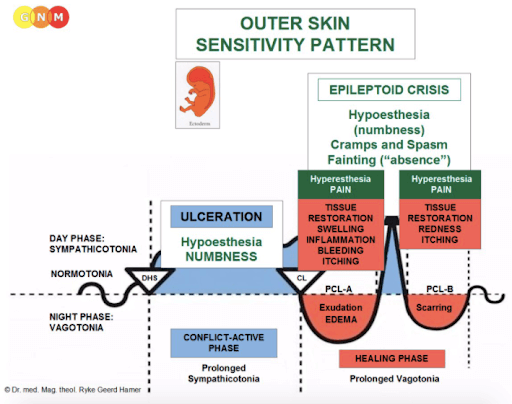
The Biological Special Program of the epidermis follows the OUTER SKIN SENSITIVITY PATTERN. There’s a conflict-active phase followed by a healing phase.
Conflict-Active Phase
During the conflict-active phase, the epidermis proliferates the cells at the area associated with the separation. This cell proliferation is microscopic and usually goes unnoticed.
As the conflict activity continues, however, the skin becomes dry, rough, flaky, pale, and cold from poor blood circulation. Eventually, the skin begins to crack causing fissures that may bleed. If an intense conflict persists for a long period of time, the skin opens at the ulcerated area.
Because of the loss of epidermal cells the sensitivity of the skin decreases. If the separation conflict is severe the skin can become completely numb (sensory paralysis). A brief reactivation of the sensory paralysis arises during the Healing Phase.
A typical symptom of the conflict-active phase is a short-term memory loss, which serves the purpose to temporarily “forget” the one who was “torn from the skin” by blocking out the memory (in the animal world, a mother cat does no longer recognize her offspring when they are separated from her too early).
The short-term memory loss reaches into the first part of the healing phase (PCL-A). In children, poor memory shows as learning difficulties and focusing problems, nowadays labeled as Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD).
What is Baby Eczema's Healing Phase
During the first part of the healing phase (see PCL-A in image above) the irritated area of the skin is replenished through cell proliferation. The skin swells up, becomes red, inflamed, irritated, itchy, and sensitive to touch (hypersensitivity). The small fluid-filled edemas appear as blisters.
After the Epileptoid Crisis, in the second part of the healing phase (see PCL-B in image above), the blisters dry up and the skin normalizes, provided there are no conflict relapses.
The healing of the skin manifests as a SKIN RASH, termed dermatitis, eczema, hives, measles, rubella, chickenpox, rosacea, lupus, psoriasis, herpes, et cetera. Based on German New Medicine, it is all the same, namely the healing phase of a separation conflict. In this case, what is baby eczema is simple the healing phase of a separation conflict.
Skin Rash Location
An unwanted separation (not being able or allowed to embrace or hold a beloved person or a pet) typically presents itself as a skin rash on the inside of the arms, hands, fingers, or legs, while wanting to separate from a person affects predominantly the outside of the arms, hands, elbows, legs, knees, shinbones, or ankles used, figuratively, to push or kick someone away.
Depending on the exact conflict situation, focal skin rashes also appear on the head (scalp), face, lips, chest, belly, external genitals, toes, and feet (wanting or not wanting to leave a certain place), or on the back.
A widespread skin rash reveals a generalized separation conflict suffered by a person as a whole. A body rash can also be caused by poisoning, for example, from medication – without a biological conflict.
NOTE: Whether the right or left side of the body (or both sides) is affected is determined by a person’s handedness and whether the conflict is mother/child or partner-related.
Chronic & Recurring Skin Rashes
A chronic skin rash occurs due to persistent conflict relapses through setting on a track that was established when the separation conflict first took place. Thus, with hanging healing, the skin condition remains until all tracks are cleared.
A Syndrome (a concurrent, active abandonment or existence conflict) worsens the rash. During extended periods of conflict activity, the skin rash disappears. The Biological Special Program is, however, not completed!
NOTE: Topical corticosteroids used in inflammatory skin conditions interrupt the healing phase. This is why the rash reoccurs shortly after the application is discontinued.
Recurring skin rashes are also triggered by the encounter with a conflict track.
If the rash is on the hands or fingers it is called a “contact eczema” or “allergic contact dermatitis”.
Tracks that prompt the flare-up of such eczemas are, for instance, a specific fruit or vegetable, a piece of jewelry (ring or necklace), a certain body care product or perfume, or animal hair (a pet).
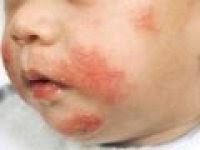
What is Baby Eczema Exactly?
Babies develop dermatitis around the mouth and on the cheeks when the mother stops breastfeeding too abruptly. The separation conflict is brought on by the loss of contact with the mother’s breast. If the first taste of commercial milk is established as a track, this causes a so-called “milk allergy”.
Since the face is supplied by the trigeminal nerve, healing of the facial skin is often accompanied by nerve pain, called trigeminal neuralgia.
How To Cure Baby Eczema at Home, Right Now
After reading and understanding:
- The role of the epidermis
- How the skin is controlled by the brain
- Biological Conflict of Separation
- The Conflict-active Phase
- The Healing Phases
As parents, we must be the observer of our children. Taking your new understanding of the human body, coupled with deep observation of your baby, you may find many hints to decipher your child’s eczema.
It is up to you to recall the genesis of your child’s story with eczema and to piece together the bits of information you gain to find what triggers/triggered this reaction. It’s true detective work! And it is all worth it for the sake of your child's health, now and long into the future.
These are the steps to cure baby eczema at home:
- Recognize: Physical health symptoms are meaningful and reveal shocks and traumas your child has experienced, as you just read in this article.
- Realize: After learning the biological meaning of your child’s symptoms, you can appreciate and realize the significance of these symptoms and that they are evidence of how your child’s body is adapting for his/her survival.
- Recall: You can examine your child’s personal history and recall the shock he/she experienced that led to the tissue adaptations he/she is currently dealing with. Dig into how this conflict affected your child’s sense of safety, and how this event is still shaping how he/she thinks and feels. When did your baby first develop eczema? What new situation was taking place at that very time?
- Release: If your child is dealing with a chronic health issue, you know there is a chronic experiential pattern that is continually being reactivated. Help your child release any situations that are keeping him/her stuck in this pattern.
- Replace/Reprogram: Your child needs to build a new way of thinking about whatever that shocking life experience was. You need to be very deliberate about how you help your child’s psyche, brain and body complete the healing phase and find closure with the triggering event. Tell your child that they are safe. Safety is a BIG deal for survival.
- Reconcile: Even though most of the “work” from the German New Medicine perspective revolves around resolving inner conflict, it is also important to examine lifestyle habits and make sure there is alignment between what you believe is best for your child and what you are actually doing.
>>If you would like to know more about how to heal your skin 100%, get the FREE eBook on the 3 secrets to heal Eczema once and for all.
Related Content
6 Natural Eczema Remedies To Heal Your Skin
Resources:
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/eczema-atopic-dermatitis.html
Germanic New Medicine – SKIN Separation conflict https://learninggnm.com/SBS/documents/skin.html

Gabriele Beland gives you the good and the bad of healing 100% any skin condition, from the inside out, using body chemistry and simple laws of health. You can listen to The Laws of Health Podcast.

Don't forget to follow us on Pinterest. Thank you for your time and reading.


